Economics Ch - 6 Class 12th (BANKING)
Ch - 6 (BANKING)
Banks
1.Commercial Banks.
2.Central Banks.
Functions of Commercial Banks :-
1.Accepts deposits from people.
2.Advance loans to people.
Functions of Central Bank :-
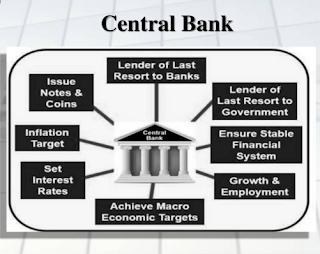
1.Bank of Issuing Notes :- Central Bank of a country has exclusive right of issuing notes . It is the sale agency of issuing notes till the beginning of 20th Century . The Central Bank are known as "Bank of Issue".
2.Banker's to the Govt. :- Central Bank is a banker , agent & financial advertisers to the govt . It maintenance the account of central and state government . Central Bank collects taxes and other payments on behalf of govt. It also give advice to the govt. on economy monetary and on a fiscal matters.
3.Banker's Bank and Supervisory Role :- Central Bank regulates and supervise the commercial banks . It accepts deposits from the commercial bank and offer from Bank Rate , Repo Rate , SRR & SLR . The ratio of these reserves are decided by Central Bank.
4.Lender of the Last Resort :- When commercial banks fails to meet their financial requirements from other sources the central bank provide their loan as lender of the last resort.
5.Custodian of Foreign Exchange :- Central Bank performs the function of "Managed Floating". Managed Floating refers to the sale and purchase of foreign exchange with a view to achieving stability of exchange rate.
6.Clearing House Function :- All Commercial Banks have their account with central bank . Therefore , the central bank can easily settled claims on various commercial banks against each other , by debit and credit entries in their accounts.
7.Control of Credit :- The principal function of the central bank is to control the supply of credit in the economy.
It implies increases or decrease in the supply of money in the economy by regulating the "Creation of Credit" by commercial banks . The central bank needs to control the supply of money to cope with the situation of inflation and deflation . During inflation , the supply of money is reduced and during deflation supply of money is increased.
Instrument to Control the Money Supply by the Central Bank
Quantitative Instruments to Control Credit Control :-
Quantitative Instruments are those instruments of credit control which focus on the overall supply of money in the economy.
1.Bank Rate :- Bank rate refers to rate of interest at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks. It relates to instant loan requirement of the commercial banks.
During Inflation -) RBI increases Bank Rate -) it increase the market rate of interest -) fall in demand for credit -) less money supply is market -) inflation is controlled
During Deflation -) RBI decreases bank rate -) it decreases the market rate of interest -) rise in demand for credit -) more money supply in market -) deflation is controlled.
2.Open Market Operations :- It refers to the sale and purchase of securities in the open market by the RBI on behalf of govt.
During Inflation -) RBI sells the securities -) RBI soaks the liquidity of cash -) fall in cash reserves of commercial banks -) fall in credit capacity of commercial banks -) fall in money supply -) inflation is controlled.
During Deflation -) RBI purchases the securities -) RBI release the liquidity of cash -) rise in cash reserves of commercial banks -) rise in credit creation capacity of commercial banks -) rise in money supply -) deflation is controlled.
3.Repo Rate - The rate at which the RBI offers short period loans to the commercial banks by buying the govt. securities in open market is called repo rate. It is also called repurchase rate.
During Inflation -) RBI increases the repo rate -) rise in cost of capital -) fall in demand for credit -) fall in supply of money by commercial banks -) inflation is controlled.
During Deflation -) RBI decreases the repo rate -) fall in cost of capital -) rise in demand for credit -) rise in supply of money by commercial banks -) deflation is controlled.
4.Reserve Repo Rate - The rate at which RBI accepts deposits from commercial banks is called 'reserve repo rate' . It is also called reverse Repurchase rate.
During Inflation -) RBI increases reserve repo rate -) more funds are parked by commercial banks with RBI -) less funds used as C.R.R. funds for creation of credit -) supply of money decreases -) inflation is controlled.
During Deflation -) RBI decreases reverse repo rate -) less funds are parked by commercial banks with RBI -) more funds used as C.R.R.funds for creation of credit -) supply of money increases -) deflation is controlled.
5.Cash Reserve Ratio (C.R.R) - It refers to the minimum percentage of a bank's total deposits required to be kept with RBI.
During Inflation -) RBI increases C.R.R.-) less money available to be used as credit by commercial banks -) money supply in market -) controlled inflation.
During Deflation - RBI decreases C.R.R.-) more money available to be used as credit by commercial banks -) more money supply in market -) controlled deflation.
6.Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) - every bank is required to maintain a fixed percentage of its assets in the form of liquid assets are called SLR.
These include :-
a)Cash
b)Gold
c)Unencumbered approved securities.
During Inflation -) RBI increases SLR -) less money available to be used -) as credit by commercial banks -) less money supply in market -) controlled inflation.
During Deflation - RBI decreases SLR -) less money available to be used as credit by commercial banks -) less money supply in market -) controlled deflation.
Quantitative Instruments of Credit Control :-
These are those instruments of credit control which focus on select sectors of the economy.
1.Margin Requirement - It refers to the difference b/w the current value of security offered for loans and the value of loan granted.
During Inflation -) RBI increases margin requirement -) fall in demand for credit -) fall in money supply by commercial banks -) inflation is controlled.
During Deflation -) RBI decreases margin requirement -) increase in demand for credit -) increase in money supply by commercial banks -) deflation is controlled.
2.Rationing of Credit - It refers to the fixation of credit quotas for different business activities.
Introduction of Credit Rationing -) decreases in the supply of credit by commercial banks -) decreases in the money supply -) inflation is controlled.
Withdrawal of Credit Rationing -) increases in the supply of credit by commercial banks -) increases in the money supply -) deflation is controlled.
Moral Suasion - It is a combination of both 'Persuasion' and 'Pressure' . The RBI tries to persuade the commercial banks to follow its directives , but if persuasion does not work , it uses the required pressure as an apex bank of country . If pressure also does not work , the RBI on use direct action.
Money Creation By Central Bank
Commercial banks are an important source to create credit in the mark . They create credit many times more than their initial deposits which demand deposit by the people . These are called primary deposits.
The process of credit creation by commercial banks can be explained a follows :-
1.The historical experience of commercial banks has shown that people do not withdrawn their money at same time.
2.If withdrawals are generally around 10% of demand deposits the banks need to keep only 10% of deposits as cash reserves.
3.If we want to calculate the total demand deposits of people it can be calculated as -
Demand Deposits = 1/C.R.R. X Cash Reserve]
C.R.R. = Cash Reserve Ratio
4.Higher the cash reserves lower will be the supply of money in market.
Let us take an example to understand the above process -
Assumptions :-
1.There is a single banking system in economy.
2.C.R.R. = 10% and it does not change.
3.Initial Deposits = 1000
........
|Rounds | Deposits | Loans | Cash R. │
| | (Rs.) | (Rs.) |(C.R.R = 10%) │
|1st Round | 1000 | 900 | 100 |
| | 900 | 810 | 90 |
| | 810 | 729 | 81 |
| Total | 10,000 | 9,000 | 1,000 |
| (and so on till excess reserve is exhausted) |
After keeping 10% as cash reserves it uses the remaining amount of deposits to lend money.
These loans are also with the bank as secondary deposits. Now , the commercial bank uses the deposits to grant loans. This process continues till total demand deposits are Rs.10,000 and cash reserves are Rs.1,000
Thus if C.R.R is 10% , initial deposits of Rs.1000 allows the bank to create demand deposits upto Rs.10,000 . So that DD = 1/C.R.R X C.R.
=1/10% X 1000
100/10 X 1000 = Rs.10,000
Credit Multiplier
In India , C.R.R. is fixed by RBI. Accordingly , credit multiplier indicates the maximum amount of money that the commercial banks can create given their cash reserves with RBI.
K = 1/C.R.R.
Where,
K = Credit Multiplier
C.R.R = Cash Reserve Ratio
Ex. If C.R.R = 10% THEN
K = 1/10% = 100/10 = 10
It implies that if CR = 10% then the commercial banks can create money 10 times of their cash reserved with the central bank.






No comments: