Economics Ch - 7 Class 12th ( Aggregate Demand , Aggregate Supply and Related Concepts )
Ch - 7 ( Aggregate Demand , Aggregate Supply and Related Concepts )
Aggregate Demand - It refers to the sum total of Expenditure on the Goods and
Services by the people of an Economy.
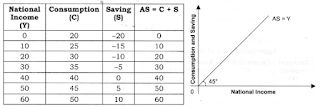
Aggregate Schedule - It is a table showing AD at different level of Income(Y).
Aggregate Curve - It is the diagram presentation of AD Schedule.
1.) There is some minimum level of Consumption even when Y=0 as some Expenditure on a Goods and Services is essential for survival use may do it from Past Saving or Borrowing.
2.) AD increases as Y(Income)
increases. This AD is Positively related to Y.
3.) At a point AD = Y.
4.) Finally, AD < Y as people
develops the habit to save more.
Components of Aggregate Demand :-
1.) Closed Economy:-
a) Two Sector Economy ( C + I
)
2.) Open Economy :-
a) Four Sector Economy
{ C + I + G + (
X - M ) }
A) Private Consumption Expenditure - When Households purchase Goods for Consumption. Accordingly this expenditure is called Private Consumption Expenditure.
B) Investment Consumption Expenditure - Producers produce goods for the purpose of Investment. Accordingly their Expenditure is called Investment Expenditure.
C) Government Expenditure -
1.) Government Consumption Expenditure - It refers to the Public Consumption Expenditure or Consumption Expenditure on behalf of the Society as a whole.
For Example - Midday Meal,etc.
2.) Government Investment Expenditure - The govt. makes investment expenditure in the development of Society. For Example - Construction of roads , Dams etc.
D) Net Export ( X - M ) - Rest of the World generates demand for our goods and services in terms of our exports , We also make import from Rest of the World. While exports ( X) increases AD of the domestic economy and Imports decreases AD of the domestic economy.
Aggregate Supply - It refers to the sum total of production as planned by the Producers during an accounting year.
Production of goods and services ---> Value Addition ----> Income Generation
Value added and income generated are identical to each other.
AS implies flow of income in the
economy during an accounting year.
Aggregate Schedule - It is the table showing the behaviour of AS corresponding to different level of Income (Y).
It must be noted that this behaviour of AS is true with respect to such economies where there is excess capacity and AS can proportionately rise whenever there is any rise in AD.
Consumption Function
Consumption - The part of income which we use to satisfy our needs is
called Consumption.
Consumption Function - The functional relationship between consumption and income is called Consumption Function.
1.) X-axis represents income and Y-axis represents Consumption.
2.) Initially; C > Y ,because even if the income level is zero the consumer will consume something either from the past saving or by borrowing.
3.) After that C = Y this is called break even point.
4.) At last C < Y because consumer start to save some part of income.
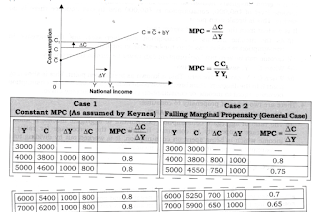
Propensity to Consume :- The relation between Consumption and Income is called Propensity to Consume.
This can be measured by two types :-
A) APC
A) APC ( Average Propensity to Consume ) - The measurement of direct ratio between Consumption and Income.
APC = C/Y
when C > Y then APC >1
MPC = Δ C/Δ Y
MPC is a straight line slope. It represents the slope of Consumption Function.
Algebraic Expression of C - Function :-
_ _
b = MPC
Y = Income
Y = C + S







No comments: