Economics Chapter - 8 Class 12th ( Short Run Equilibrium Output)
Chapter --- 8 ( Short Run Equilibrium Output)
AS = AD Approach
When AS = AD Corresponding to full employment is known as equilibrium in economy.
Assumptions -
Aggregate demand - It is the sum total of expenditure by an economy during an accounting year . It has two Components:- C + I
Consumption (C) :- It has positive relation with the income.
Investment ( I ) :- It is assumed to be autonomous . It remains constant . It does not change with the change in income.
Equilibrium Of AS& AD :-
X - axis shows the income and Y - axis shows AD.
When AS >AD Supply of goods and services is more compared to demand. Therefore, the stock of the producers would remains unsold . So producers will produce less goods and AS becomes equal to AD.
When AS< AD , demand of goods and services is more than the supply . Therefore the producer will suffer the unfulfilled demand of the consumers. So producer will produce more and AS will becomes equal to AD .
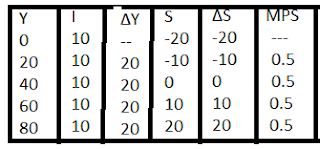
S= I Approach :-
According to S= I approach , when saving is equal to investment, then this situation is called equilibrium.
S refer to leakage because it discourage the production activity in the economy.
Assumptions :-
Equilibrium of S = I
When S > I , more saving means less investment . It leads to less income and it leads to less saving.So, saving will become equal to investment.
When S < I, less saving means more investment.It leads to more income and it leads to more saving. So Saving will became equal to Investment.
INVESTMENT MULTIPLIER
K has positive relation with M.P.C.because consumption of one person increases the income of other person.
Relation of K with Marginal Property to save
K has negative relation with M.P.C.because saving of one person decreases the income of other person.
Maximum value of Multiplier
Minimum value of Multiplier
Forward Action and Backward Action of Multiplies:-
Multiplier action is forward when there is a multiple increase in income caused by an increase in investment.
Multiplies actions background when there is a multiple decreases in income caused by decrease in investment.











No comments: